Table of Contents
Learn the fundamentals of gas air conditioning (AC) by reading “Gas AC Usage Explained: Understanding Refrigerant Consumption.” This guide explains how the refrigerants in your air conditioning system work to keep your room cool. Discover the significance of refrigerants, their cycle through the air conditioning machine, and why efficient use is crucial. Learn about typical influences on refrigerant levels and easy techniques to keep them there. Understand the fundamentals of gas air conditioning operation whether you’re a homeowner or an HVAC enthusiast. This article provides clear explanations to help you make well-informed decisions on the maintenance and durability of your air conditioning system. Lets have a detail look on the gas ac usage and refrigerant consumption.
if you are facing the problem of your AC blowing warm air . we have a solution with our ultimate gudie having 9 reasons and fixes lets delve into this detailed guide.
Essential Operation:
Heat transfer during the refrigeration cycle is the basis for how gas air conditioning systems work. To take heat from indoor air and release it outdoors, refrigerant gas goes through a cycle of compression, condensation, expansion, and evaporation. The receiver drier, also known as the accumulator, is essential to this operation. By eliminating any moisture or impurities from the system, the receiver drier serves as a storage tank for the refrigerant, preserving the system’s longevity and efficiency.
It’s important to realize that the amount of refrigerant needed for an air conditioning system can vary depending on several factors, including the size of the room being cooled, the surrounding climate, and the system’s exact design. However, it’s usually expressed in pounds or kilos. The system must be charged with the appropriate amount of refrigerant for best results and energy efficiency. Refrigerant excesses can result in ineffective cooling and possible harm to the AC system’s parts.
Additionally, the correct amount of refrigerant must be maintained for the system to operate efficiently. Over time, refrigerant leaks from the system might occur, lowering its cooling ability. Regular maintenance and inspections by trained specialists can assist in locating and fixing any leaks quickly.
Refrigerant
Refrigerants are essential parts of air conditioning systems that control temperature in enclosed areas like automobiles, residences, and commercial buildings. These chemical substances, which efficiently absorb and release heat at low temperatures, include hydrochlorofluorocarbons (HCFCs) like R-22, hydrofluorocarbons (HFCs) like R-410A, and hydrocarbons like R-290 (propane) and R-600a (isobutane).
Refrigerants are essential to maintaining pleasant cabin temperatures in car air conditioning systems. Still, there’s a problem when cars are parked. The AC system still uses refrigerant gas when it is not in use, just more slowly. To make up for the refrigerant loss while the engine is running, this continual usage, combined with the inefficiencies of older refrigerants like R-22, can cause an increase in fuel consumption.
Refrigerant technology has advanced due to worries about fuel use; newer formulas, like R-410A, promise improved efficiency and environmental friendliness. Additionally, AC systems must be properly maintained to reduce refrigerant leakage and maximize fuel efficiency. Drivers can lessen the effect on fuel usage when parked and operating their air conditioning systems by fixing leaks and ensuring there is enough refrigerant.
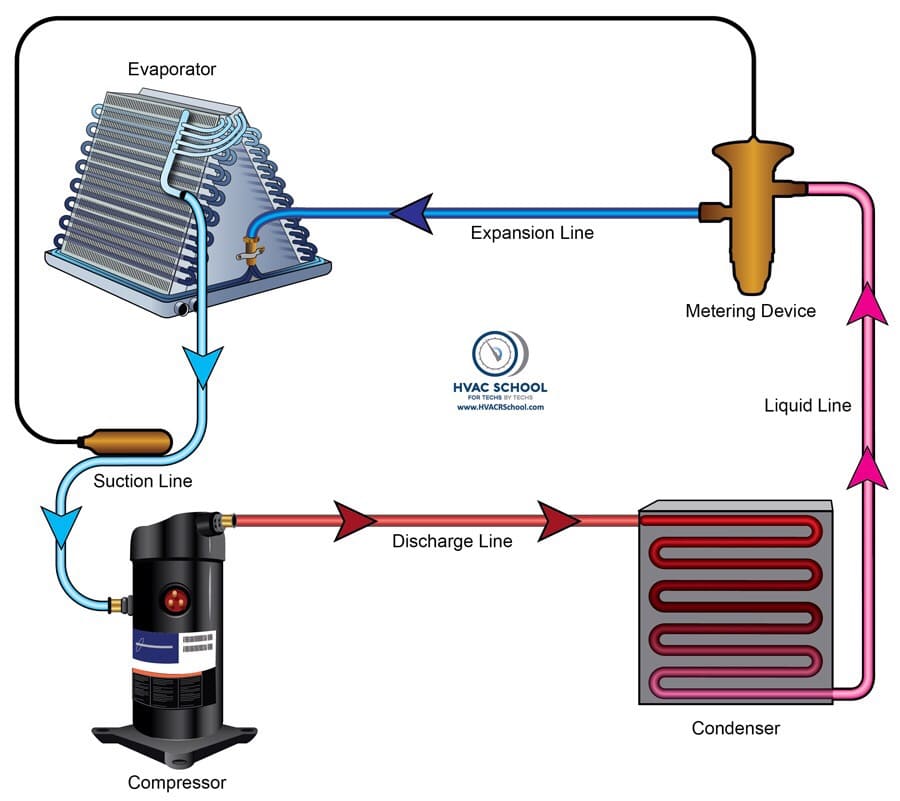
Refrigerant Circuit
The refrigerant circuit is essential for effective cooling in an air conditioning system. This well-thought-out closed-loop system consists of an evaporator, condenser, expansion valve, and compressor. An essential component is the compressor, which starts the refrigerant gas on its journey by compressing it. The gas condenses through the condenser, releasing heat and changing into a high-pressure liquid. After going through the expansion valve, the liquid’s pressure drastically reduces, allowing it to evaporate quickly in the evaporator. By absorbing heat from the surrounding air, this evaporation cools the air. After that, the cooled air is moved throughout the interior to create a cozy atmosphere.
The quantity of gas an air conditioning system uses is determined by several factors, including system size, efficiency, and capacity. A certain amount of refrigerant is usually needed for an air conditioning system to function at its best. Overcharging or undercharging the system may result in damage or inefficiencies.
Furthermore, the AC system’s efficiency may impact a car’s gas mileage. A well-maintained AC system runs at peak efficiency and puts less load on the engine, improving gas mileage. For this reason, maintaining the refrigerant circuit properly is crucial for fuel economy and cooling efficiency.
want more details about refrigent circuit here is the detail article
Consumption Factors
Several factors influence the amount of refrigerant gas used in air conditioning systems. One important reason is leakage, which causes the AC system to lose refrigerant steadily over time. There are a number of potential causes for this leakage, including corrosion, aging, and even faulty air conditioning system installation. Small leaks can worsen as the compressor compresses the refrigerant, lowering performance and efficiency.
Furthermore, evaporation and degradation are significant factors in refrigerant use. Refrigerants are stable inside the system, but over time, they can lose their efficiency because of impurities, temperature changes, or chemical interactions. This deterioration highlights the need for routine AC maintenance procedures. Through coil cleaning, filter replacement, and leak detection, users can minimize refrigerant loss and guarantee peak efficiency.
Refrigerant consumption is also directly impacted by the size and usage patterns of the air conditioning system. More refrigerant is usually needed for larger air conditioning systems to operate effectively. Furthermore, the system may be overworked or exposed to extremely hot or low temperatures, increasing the need for gas air conditioning. Thus, keeping an air conditioning system efficient and long-lasting requires understanding these consumption parameters.
A system’s size and utilization, leakage, evaporation, maintenance procedures, and other factors all play a significant role in how much refrigerant gas is used in an air conditioning system. By taking proactive measures to address these variables, users can reduce operational expenses and environmental impact while maximizing the longevity and performance of their air conditioning systems.

Recharging
Maintaining the longevity and efficiency of the air conditioning system requires regular recharging. The operation of the gas ac use system may be negatively impacted when refrigerant levels drop, whether due to leaks or other causes. This affects both fuel economy and interior comfort levels in the car.
Insufficient refrigerant levels when using the air conditioning system can stress the compressor, potentially causing damage and increasing fuel usage. As a result, routine AC system inspection and recharging are crucial maintenance duties.
Technicians ensure the air conditioning system runs efficiently by quickly fixing leaks and topping off refrigerant levels to ideal levels. This improves passenger comfort while also increasing fuel economy.
Using gas air conditioning, especially when the system has low refrigerant levels, might result in inefficiencies and increased fuel usage. Therefore, regular maintenance, including recharging and repairs, is essential to maintaining the AC system in good shape for optimal vehicle performance and fuel efficiency.
Environmental Impact
Due to the growing awareness of environmental issues, the effects of refrigerants on the environment are becoming a major concern. R-22 and other conventional refrigerants have been phased out because of their negative effects on the ozone layer and their role in global warming. As a result, the HVAC sector has switched to using R-410A and other more environmentally friendly substitutes.
These more recent refrigerants align with attempts to lessen climate change because they have less potential for global warming and ozone depletion. Incorporating them into air conditioning systems results in effective cooling and reduces the environmental impact of HVAC operations.
Gas air conditioners have also changed to be more environmentally friendly. Greener refrigerants, such as R-410A, are used to minimize environmental damage while maintaining the cooling process’s efficiency. Knowing that these eco-friendly refrigerants contribute less to global warming and ozone depletion than their predecessors, homeowners and businesses alike are more likely to run their air conditioners with them.
The transition to greener refrigerants is in line with initiatives to improve the fuel efficiency of air conditioning systems. These environmentally friendly substitutes can help air conditioning equipment run more smoothly, consume less energy, and emit fewer greenhouse gases.
In conclusion, using eco-friendly refrigerants, like R-410A, is essential for ensuring that air conditioning systems run smoothly, reducing environmental effects, increasing fuel economy, and encouraging the use of greener cooling technology.
